Office - D:\Practice Projects\vasanth.github.io-main
https://www.javatpoint.com/browser-object-model
https://javascript.info/alert-prompt-confirm
https://javascript.info/
Introduction
What is JavaScript?
What Is AJAX?
Developer Essentials
The development workflow
Selecting the right tools for the job
Just enough HTML and CSS
Understanding objects
Understanding variables
Making comparisons
Understanding events
Starting to Code
Writing your first script
Internal vs. external scripts
Using comments in scripts
Using the NoScript tag in HTML
Interacting with Users
Creating alert dialogs
Understanding conditional statements
Getting confirmations from users
Creating prompts for users
Understanding functions
function showMessage () {
alert ( 'Hello everyone!' );
}
showMessage ();
function showMessage (from , text ) {
from = '*' + from + '*' ; // make "from" look nicer
alert ( from + ': ' + text );
}
let from = "Ann" ;
showMessage (from , "Hello" ); // *Ann*: Hello
function myFunction ( a , b ) {
return a + b ;
}
alert ( myFunction (5 ,10 ) );
Image rollover function
< img width ="400px" height ="400px" src ="img.jpg" id ="image" onmouseover =" newPicture () "
onmouseout =" oldPicture () " >
function newPicture () {
document .getElementById ("image" ).src ="img1.jpg" ;
}
function oldPicture () {
document .getElementById ("image" ).src ="img2.jpg" ;
}
Making links smarter
Using switch/case statements
let a = 2 + 2 ;
switch (a ) {
case 3 :
alert ( 'Too small' );
break ;
case 4 :
alert ( 'Exactly!' );
break ;
case 5 :
alert ( 'Too big' );
break ;
default :
alert ( "I don't know such values" );
}
Handling errors
try {
alert ('Start of try runs' ); // (1) <--
lalala ; // error, variable is not defined!
alert ('End of try (never reached)' ); // (2)
} catch (err ) {
alert (`Error has occurred!` ); // (3) <--
}
JavaScript Language Essentials
Getting started
Creating loops
let i = 0 ;
while (i < 3 ) { // shows 0, then 1, then 2
alert ( i );
debugger ;
i ++;
}
for (let i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i ++) { // shows 0, then 1, then 2
alert (i );
}
Passing values to functions
Detecting objects
let user = { // an object
name : "John" , // by key "name" store value "John"
age : 30 // by key "age" store value 30
};
alert (user .name );
alert (user .age );
Reading arrays
Returning values from functions
Writing arrays
let fruits = ["Apple" , "Orange" , "Plum" ];
alert ( fruits [0 ] ); // Apple
alert ( fruits [1 ] ); // Orange
alert ( fruits [2 ] ); // Plum
Building do and while loops
Re-using functions
Creating Rollovers and More
Creating a basic image rollover
How to write a better rollover
Creating a three-state rollover
Making rollovers accessible and 508 compliant
Making disjointed rollovers
Displaying random images
Building Smarter Forms
Getting started
Creating jump menus
< select id ="jm1" class ="jumpmenu" >
< option value ="" ></ option >
< option value ="http://google.com/" > Google</ option >
< option value ="http://yahoo.com/" > Yahoo!</ option >
< option value ="http://ask.com/" > Ask.com</ option >
</ select >
function initJumpMenus () {
// Turns all <select> elements with the 'jumpmenu' class into jump menus
var selectElements = document .getElementsByTagName ("select" );
for ( i = 0 ; i < selectElements .length ; i ++ ) {
// Check for the class and make sure the element has an ID
if ( selectElements [i ].className == "jumpmenu" && document .getElementById (selectElements [i ].id ) != "" ) {
jumpmenu = document .getElementById (selectElements [i ].id );
jumpmenu .onchange = function () {
if ( this .options [this .selectedIndex ].value != '' ) {
// Redirect
location .href =this .options [this .selectedIndex ].value ;
}
}
}
}
}
window .onload = function () {
initJumpMenus ();
}
Creating dynamic menus
Requiring fields
Validation - 1 (Before this check Dom Events) < form name ="f1" onsubmit =" return validation () " >
Name: < input type ="text" name ="name" >< br />
Password:< input type ="password" name ="password" />< br />
Re-enter Password:< input type ="password" name ="password2" />< br />
< input type ="submit" >
</ form >
function validation (){
var name =document .f1 .name .value ;
var firstpassword =document .f1 .password .value ;
var secondpassword =document .f1 .password2 .value ;
if (name ==null || name =="" ){
alert ("Name can't be blank" );
return false ;
}
//pwd
if (firstpassword ==secondpassword ){
alert ("Done!" );
return true ;
}
else {
alert ("password must be same!" );
return false ;
}
}
mobile , mail
function phonenumber (mobile )
{
if (!mobile .match ('[0-9]{10}' )) {
alert ("Please put 10 digit mobile number" );
return ;
}
}
function ValidateEmail (mail )
{
if (/ ^ \w + ([ \. - ] ? \w + ) * @\w + ([ \. - ] ? \w + ) * ( \. \w {2,3} ) + $ / .test (mail ))
{
return (true )
}
alert ("You have entered an invalid email address!" )
return (false )
}
remove node / element
< h2 > The remove() Method</ h2 >
< p id ="demo" > Click "Remove", and this paragraph will be removed from the DOM.</ p >
< button onclick =" myFunction () " > Remove</ button >
function myFunction () {
const element = document .getElementById ("demo" );
element .remove ();
}
Add Node
< ul id ="myList" >
< li > Coffee</ li >
< li > Tea</ li >
</ ul >
< button value ="submit" onclick =" test () " > test</ button >
function test ()
{
// Create a "li" element:
const newNode = document .createElement ("li" );
// Create a text node:
const textNode = document .createTextNode ("Water" );
// Append text node to "li" element:
newNode .appendChild (textNode );
// Insert before existing child:
const list = document .getElementById ("myList" );
list .insertBefore (newNode , list .children [0 ]);
}
Key Events
document.addEventListener ('keypress' , (event ) => {
var name = event .key ;
var code = event .code ;
// Alert the key name and key code on keydown
alert (`Key pressed ${ name } \r\n Key code value: ${ code } ` );
}, false ); Window Events
< body onload =" alert ('Hello window') " >
Mouse Events
< button type ="button" onmouseover =" alert ('You have placed mouse pointer over a button!'); " > Place Mouse Over Me</ button >
< a href ="#" onmouseover =" alert ('You have placed mouse pointer over a link!'); " > Place Mouse Over Me</ a >
Cookie
< form name = "myform" action = "" >
Enter name: < input type = "text" name = "customer" />
< input type = "button" value = "Set Cookie" onclick = " WriteCookie (); " />
</ form >
function WriteCookie () {
if ( document .myform .customer .value == "" ) {
alert ("Enter some value!" );
return ;
}
Cross-checking fields
Displaying more informative errors
Verifying radio button selections
Setting one field with another field
Verifying email addresses
Handling Events
Responding to window events
Responding to mouse movements
Responding to mouse clicks
Responding to onBlur form events
Responding to onFocus form events
Responding to keyboard events
Working with Cookies
Demystifying cookies
Writing a cookie
Reading a cookie
Displaying a cookie
Counting with cookies
Deleting cookies
Handling multiple cookies
Cookies in action
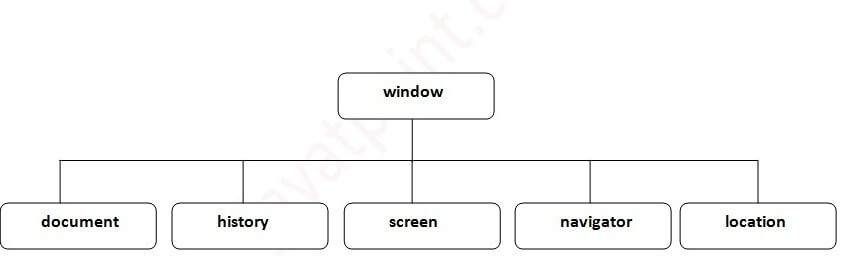
The DOM, Nodes, and Objects
Here’s a picture of links that allow for travel between DOM nodes:
Let’s discuss them in more detail.
The topmost tree nodes are available directly as document properties:
<html> = document.documentElementThe topmost document node is document.documentElement. That’s the DOM node of the <html> tag. <body> = document.bodyAnother widely used DOM node is the <body> element – document.body. <head> = document.headThe <head> tag is available as document.head.
The HTML DOM Document Object The document object represents your web page.
If you want to access any element in an HTML page, you always start with accessing the document object.
<!-- Normal Browser Events -->
< input type ="button" onclick =" alert ('Click!') " value ="Button" >
< button onclick =" alert ( this . innerHTML ) " > Click me</ button >
<!-- DOM -->
<!-- By ID -->
Enter No:< input type ="text" id ="number" name ="number" />< br />
< input type ="button" value ="squre" onclick =" getcube () " />
< br />
<!-- by Name -->
val:< input type ="text" name ="test" value ="squre" />
< input type ="button" onclick =" totalelements () " value ="Total Genders" >
< br />
<!-- getElementsByTagName -->
< h2 > This is h2 tag</ h2 >
< h3 > This is h3 tag</ h3 >
< h3 > This is h3 tag</ h3 >
< button onclick =" counth2 () " > count h2</ button > < br />
< button onclick =" counth3 () " > count h3</ button >
< br />
<!-- Javascript innerText Example -->
< form name ="myForm" >
< input type ="password" value ="" name ="userPass" onkeyup =" validate () " >
Strength:< span id ="mylocation" > no strength</ span >
</ form >
< form name ="myForm2" >
< input type ="password" value ="" name ="userPass" onkeyup =" validate1 () " >
Strength:< span id ="mylocation1" > no strength</ span >
</ form >
function getcube (){
var number =document .getElementById ("number" ).value ;
alert (number *number );
}
function totalelements ()
{
var val =document .getElementsByName ("test" )[0 ].value ;
alert ("value is :" +val );
}
function counth2 (){
var totalh2 =document .getElementsByTagName ("h2" );
alert ("total h2 tags are: " +totalh2 .length );
}
function counth3 (){
var totalh3 =document .getElementsByTagName ("h3" );
alert ("total h3 tags are: " +totalh3 .length );
}
function validate () {
var msg ;
if (document .myForm .userPass .value .length >5 ){
msg ="good" ;
}
else {
msg ="poor" ;
}
document .getElementById ('mylocation' ).innerText =msg ;
}
function validate1 () {
var msg ;
if (document .myForm2 .userPass .value .length >5 ){
msg ="good" ;
}
else {
msg ="poor" ;
}
document .getElementById ('mylocation1' ).innerText =msg ;
}
Understanding the DOM
Adding nodes to the DOM
Deleting nodes from the DOM
Deleting specific nodes
Inserting nodes into the DOM
Replacing nodes in the DOM
Working with Dates and Times
// current date
let date2 = new Date ();
// the hour in your current time zone
alert ( date2 .getHours () ); // if 6 pm it will show 18
alert ( date2 .getMinutes () );
alert ( date2 .getDate () );
const today = new Date ();
let yyyy = today . getFullYear ();
let mm = today .getMonth () + 1 ; // Months start at 0!
let dd = today .getDate ();
if (dd < 10 ) dd = '0' + dd ;
if (mm < 10 ) mm = '0' + mm ;
const formattedToday = dd + '/' + mm + '/' + yyyy ;
alert (formattedToday );
const formattedToday2 = yyyy + '/' + mm + '/' + dd ;
alert (formattedToday2 );
Displaying dates
Displaying times
Creating a countdown
Creating slideshows
< input type ="button" onclick =" setSlides ( 1 ) " value ="Show Slide" />
< div class ="images-slideshow" >
< div class ="imageSlides fade" >
< img src ="img1.jpg" >
</ div >
< div class ="imageSlides fade" >
< img src ="img2.png" >
</ div >
< div class ="imageSlides fade" >
< img src ="img3.jpg" >
</ div >
< a class ="slider-btn previous" onclick =" setSlides ( -1 ) " > ❮</ a >
< a class ="slider-btn next" onclick =" setSlides ( 1 ) " > ❯</ a >
</ div >
var currentIndex = 0 ;
displaySlides (currentIndex );
function setSlides (num ) {
displaySlides (currentIndex += num );
}
function displaySlides (num ) {
var x ;
var slides = document .getElementsByClassName ("imageSlides" );
//To show next slide after 3 right click (to start showing from begin )
if (num > slides .length )
{
currentIndex = 1
}
//To show next slide after 3 left click (to start showing from begin )
if (num < 1 ) {
currentIndex = slides .length
}
//to show in same line
for (x = 0 ; x < slides .length ; x ++) {
slides [x ].style .display = "none" ;
}
//to move next image
//display block property helps us to set our layout in proper structure
slides [currentIndex - 1 ].style .display = "block" ;
}
Real-World Applications of JavaScript
Creating sliding menus
Creating pop-up menus
Creating slideshows with captions
Creating a stylesheet switcher
2.6 , 2.7 , 2.13 ,2.14 , 2.16 , 2.17 , 2.18
4.1 , 4.3 , 4.4 , 4.5 , 5.4 ,5.5 , 5.7 , 5.12
7. 2 , 8.1 , 9.1 , 9.2 , 9.3
10.1
JavaScript provides methods:
JSON.stringify to convert objects into JSON.JSON.parse to convert JSON back into an object.let student = {
name : 'John' ,
age : 30 ,
isAdmin : false ,
courses : ['html' , 'css' , 'js' ],
spouse : null
};
let json = JSON .stringify (student );
alert (json );
let userData = '{ "name": "John", "age": 35, "isAdmin": false, "friends": [0,1,2,3] }' ;
let user = JSON . parse ( useralert ( user. friends[ 1 ] ) ;
class Animal {
constructor (name ) {
this .speed = 0 ;
this .name = name ;
}
run (speed ) {
this .speed = speed ;
alert (` ${this .name } runs with speed ${this .speed } .` );
}
stop () {
this .speed = 0 ;
alert (` ${this .name } stands still.` );
}
}
let animal = new Animal ("My animal" );
class Rabbit extends Animal {
test () {
alert (` ${this .name } test inheritance!` );
}
}
let rabbit = new Rabbit ("White Rabbit" );
rabbit .run (5 ); // White Rabbit runs with speed 5.
rabbit .hide (); // White Rabbit hides!
Note: The document object represents an html document. It forms DOM (Document Object Model).
https://javascript.info/
The visitor can type something in the prompt input field and press OK. Then we get that text in the result. Or they can cancel the input by pressing Cancel or hitting the Esc key, then we get null as the result.
The call to prompt returns the text from the input field or null if the input was canceled.
For instance:
let age = prompt ( 'How old are you?' , 100 ) ;
alert ( ` You are ${ age} years old! ` ) ;
let age = prompt ('How old are you?' , 100 );
alert (`You are ${ age } years old!` ); // You are 100 years old!
let isBoss = confirm ("Are you the boss?" );
-------------------------
Numeric conversion happens in mathematical functions and expressions automatically.
For example, when division / is applied to non-numbers:
let str = "123" ;
alert ( typeof str ) ;
let num = Number ( str ) ;
alert ( typeof num ) ;
https://javascript.info/javascript-specials
let age = prompt ( 'Your age?' , 18 ) ;
switch ( age ) {
case 18 :
alert ( "Won't work" ) ;
break ;
case "18" :
alert ( "This works!" ) ;
break ;
default :
alert ( "Any value not equal to one above" ) ;
}
let user = {
name : "John" ,
age : 30 ,
sayHi () {
// "this" is the "current object"
alert (this .name );
}
};
user .sayHi (); // John



Comments
Post a Comment